#include "include/jicmpsa.h"
Detailed Description
Internet Control Message Protocol Security Association (ICMPSA)
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Control_Message_Protocol
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is one of the main protocols of the internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, like routers, to send error messages indicating, for example, that a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached. ICMP can also be used to relay query messages.[1] It is assigned protocol number 1.[2] ICMP[3] differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications (with the exception of some diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute)
ICMP_STRUCT ICMP datagram structure
Header
The ICMP header starts after the IPv4 header and is identified by IP protocol number '1'. All ICMP packets have an 8-byte header and variable-sized data section. The first 4 bytes of the header have fixed format, while the last 4 bytes depend on the type/code of that ICMP packet
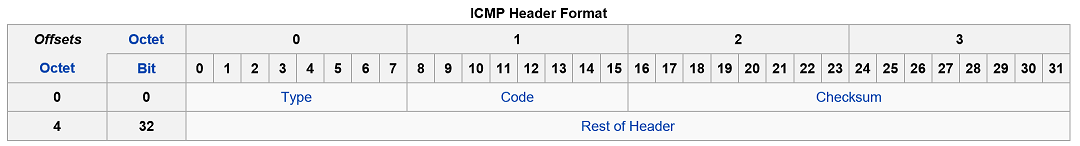
Type
ICMP type, see Control messages
Code
ICMP subtype, see Control messages
Checksum
Error checking data, calculated from the ICMP header and data, with value 0 substituted for this field. The Internet Checksum is used, specified in RFC 1071
Rest of Header
Four-bytes field, contents vary based on the ICMP type and code
Data
ICMP error messages contain a data section that includes the entire IPv4 header, plus the first eight bytes of data from the IPv4 packet that caused the error message. The ICMP packet is then encapsulated in a new IPv4 packet.[1] This data is used by the host to match the message to the appropriate process. If a higher level protocol uses port numbers, they are assumed to be in the first 64 data bits of the original datagram's data
The variable size of the ICMP packet data section has been exploited. In the "Ping of death", large or fragmented ping packets are used for denial-of-service attacks. ICMP can also be used to create covert channels for communication. These channels are known as ICMP tunnels
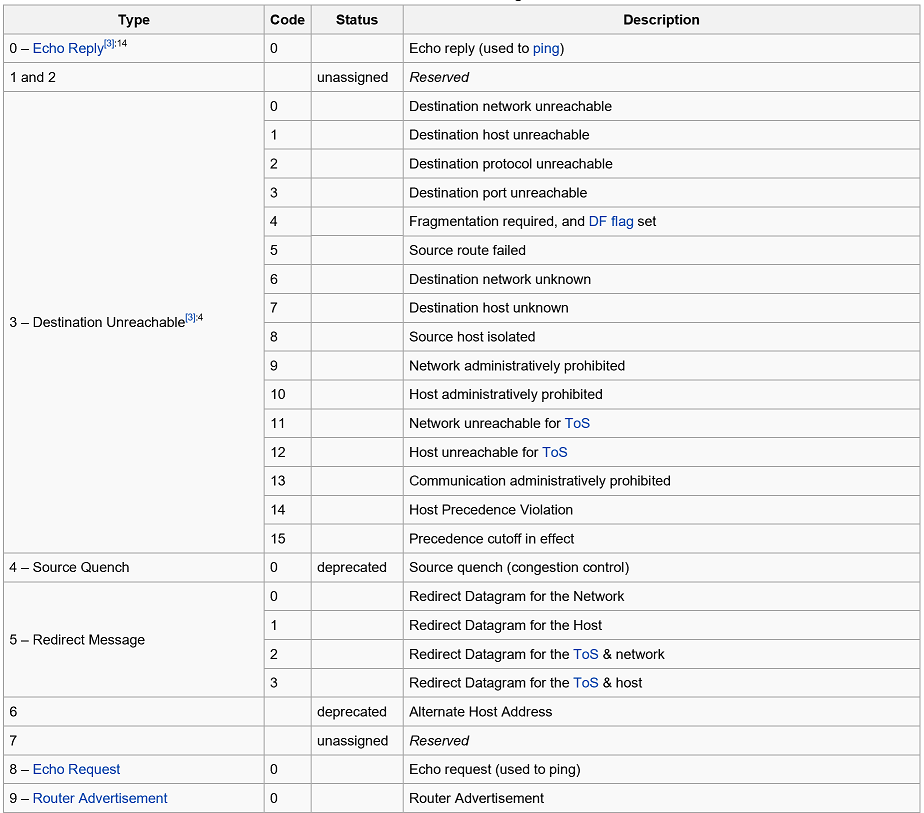
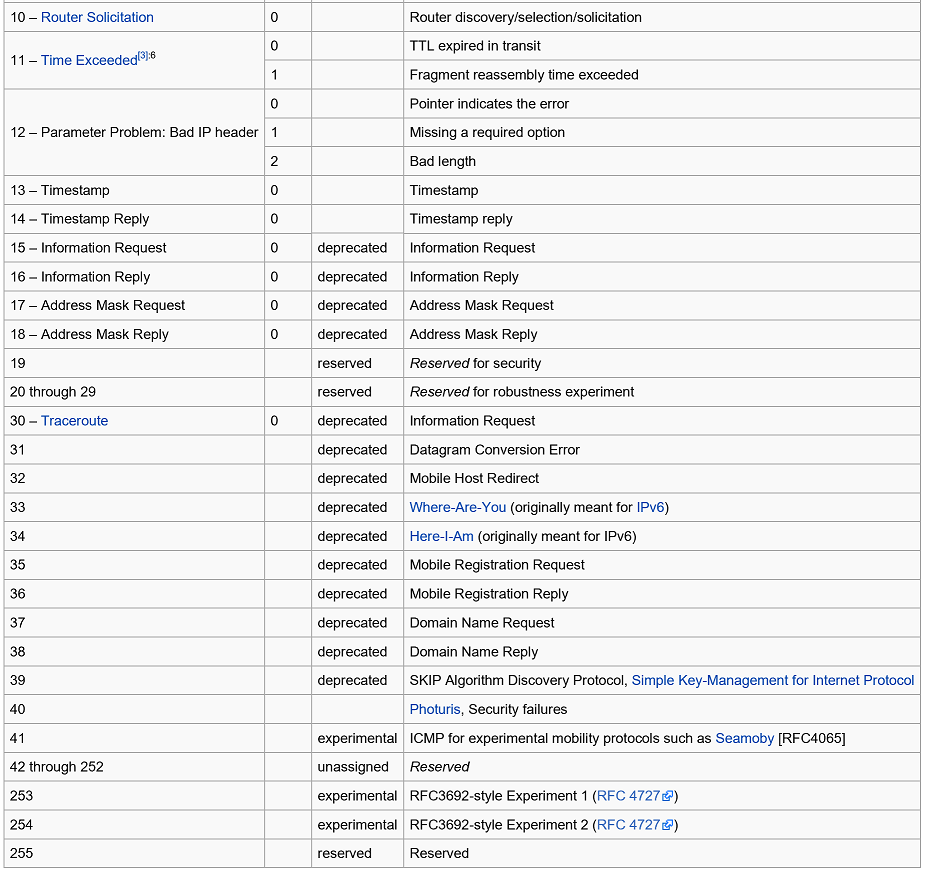
Control Messages
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Control_Message_Protocol_version_6
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) is the implementation of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). ICMPv6 is defined in RFC 4443.[1] ICMPv6 is an integral part of IPv6 and performs error reporting and diagnostic functions (e.g., ping), and has a framework for extensions to implement future changes
Several extensions have been published, defining new ICMPv6 message types as well as new options for existing ICMPv6 message types. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a node discovery protocol in IPv6 which replaces and enhances functions of ARP.[2] Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND) is an extension of NDP with extra security. Multicast Router Discovery (MRD) allows discovery of multicast routers
For API Documentation:
- See also
- ProtocolPP::jprotocol
- ProtocolPP::jarray
- ProtocolPP::jenum
For Additional Documentation:
The source code contained or described herein and all documents related to the source code (herein called "Material") are owned by John Peter Greninger and Sheila Rocha Greninger. Title to the Material remains with John Peter Greninger and Sheila Rocha Greninger. The Material contains trade secrets and proprietary and confidential information of John Peter Greninger and Sheila Rocha Greninger. The Material is protected by worldwide copyright and trade secret laws and treaty provisions. No part of the Material may be used, copied, reproduced, modified, published, uploaded, posted, transmitted, distributed, or disclosed in any way without prior express written consent of John Peter Greninger and Sheila Rocha Greninger (both are required)
No license under any patent, copyright, trade secret, or other intellectual property right is granted to or conferred upon you by disclosure or delivery of the Materials, either expressly, by implication, inducement, estoppel, or otherwise. Any license under such intellectual property rights must be express and approved by John Peter Greninger and Sheila Rocha Greninger in writing
Licensing information can be found at www.protocolpp.com/license with use of the binary forms permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
- Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution
- Any and all modifications must be returned to John Peter Greninger at GitHub.com https://github.com/jpgreninger/protocolpp for evaluation. Inclusion of modifications in the source code shall be determined solely by John Peter Greninger. Failure to provide modifications shall render this license NULL and VOID and revoke any rights to use of Protocol++®
- Commercial use (incidental or not) requires a fee-based license obtainable at www.protocolpp.com/shop
- Academic or research use requires prior written and notarized permission from John Peter and Sheila Rocha Greninger
Use of the source code requires purchase of the source code. Source code can be purchased at www.protocolpp.com/shop
- US Copyrights at https://www.copyright.gov/
- TXu002059872 (Version 1.0.0)
- TXu002066632 (Version 1.2.7)
- TXu002082674 (Version 1.4.0)
- TXu002097880 (Version 2.0.0)
- TXu002169236 (Version 3.0.1)
- TXu002182417 (Version 4.0.0)
- TXu002219402 (Version 5.0.0)
- TXu002272076 (Version 5.2.1)
- TXu002383571 (Version 5.4.3)
The name of its contributor may not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission and licensing
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER AND CONTRIBUTOR "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- include/jicmpsa.h